Steel is known for being lightweight but strong, making it suitable for a variety of industries and applications. Next to plastic and paper, steel is one of the most common materials seen in products used in our everyday lives.
In the construction industry, steel is used in the creation of buildings and other structures for strength. Manufacturing processes, such as for cars, airplanes, and kitchen appliances, also rely on steel for production. Last but not least, steel is imperative for communication as it is used in the creation of transmission and cell phone towers.
Steel Manufacturing Process
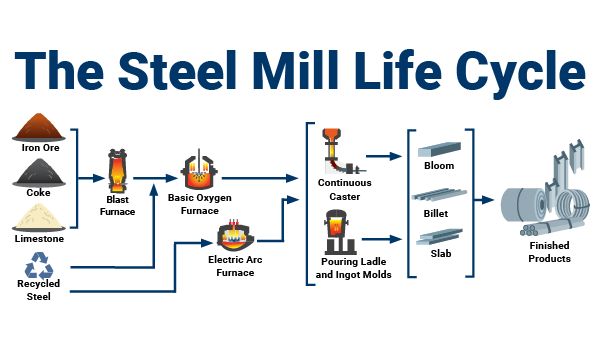
The steel manufacturing process can be divided into six steps: Making the iron, primary steelmaking, secondary steelmaking, casting, primary forming, and secondary forming.
Step 1: Making the Iron
Steel is a metal alloy made of iron and carbon. Thus, the steel manufacturing process starts by making iron. To do this, limestone, coke, and iron ore are combined and put into a blast furnace. The elements are melted together to create a hot metal known as molten iron.

Scrap metal is dropped via a scrap bucket into the electric arc furnace.
Step 2: Primary Steelmaking
The second step of the steel manufacturing process can be completed with two different pieces of equipment: a basic oxygen furnace and an electric arc furnace. With a basic oxygen furnace, the molten metal produced in step 1 is infused with scrap steel. Then, oxygen is forced through the furnace to remove the impurities in the molten iron. With an electric arc furnace, as the name suggests, electricity is forced through the furnace to purify the iron. The completion of step 2 results in raw steel.
Step 3: Secondary Steelmaking
Just like there are different grades and families of stainless steel, there are also different types of regular steel. The different grades are determined by the elements that remain in the metal at the completion of the manufacturing process. Secondary steelmaking refines the composition of the steel to create the desired grade. This is done with different techniques such as stirring and ladle injections.
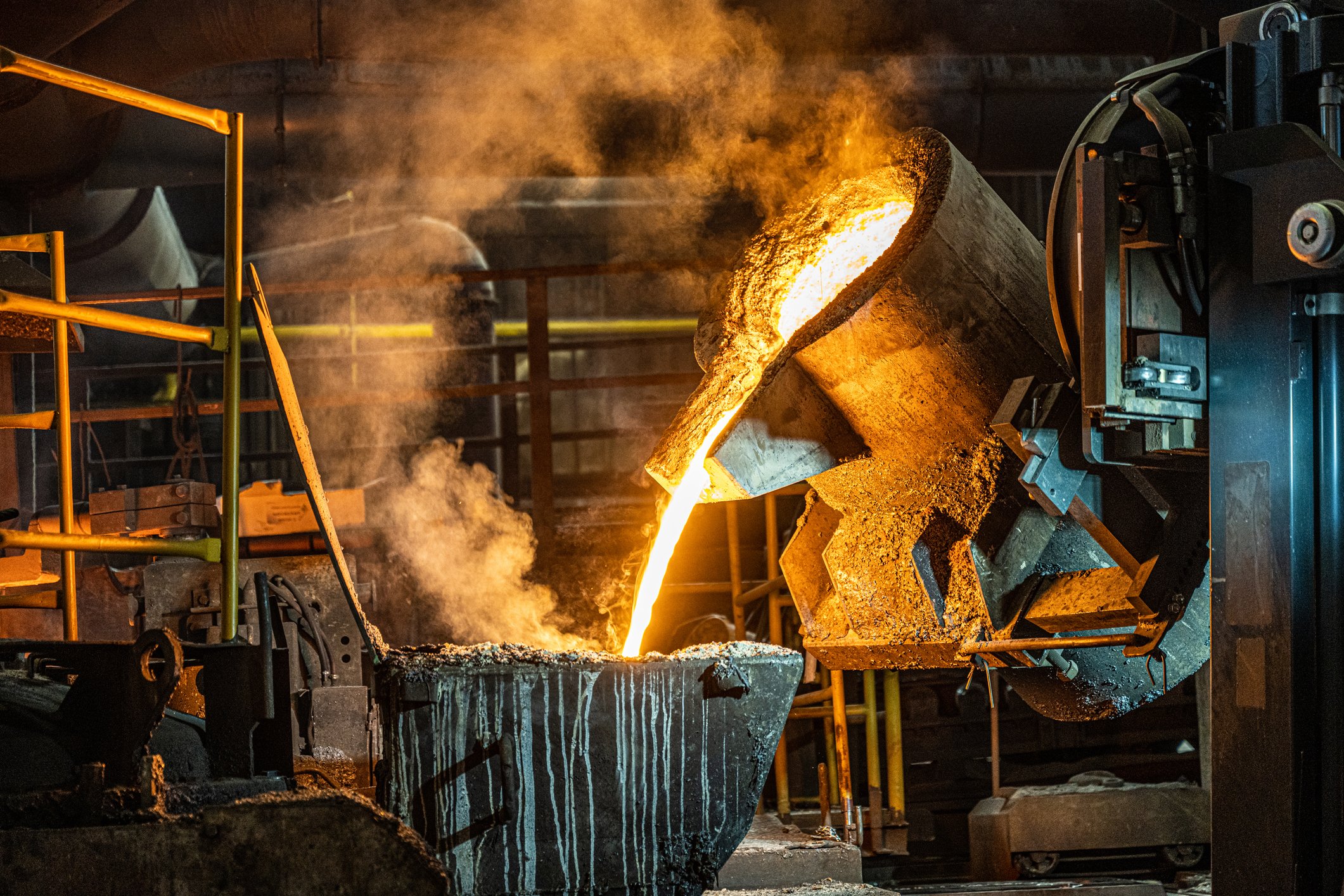


Pouring slag, the impurities that float to the top during the melting process, into a receptacle.
Step 4: Casting
During the fourth step of steel manufacturing, molten iron is cast into molds for cooling. This process starts to set the shape of the steel and causes a thin, hard shell to form. The strands of the shell are malleable and can be worked into the desired shape of flat sheets, beams, wires, or thin strips.
Step 5: Primary Forming
Primary forming continues the shaping process. A hot roller is used to fine-tune the casting. The steel is molded into the desired shape and surface finish. Some examples include bloom, billet, and slab.

Cutting billets to length using torches on the continuous caster.
Step 6: Secondary Forming
The final step of the steel manufacturing process creates the final shape and properties of the steel. Secondary forming is accomplished with different methods such as shaping (cold rolling methods), machining (drilling), joining (welding), coating, heat treatment, and surface treatment. At the completion of step 6, the steel is fully shaped, formed, and ready for use and processing in various applications.
Dixon Products for Steel Mills
The harsh environment and extreme temperatures encountered in steel mills during the steel manufacturing process require high-quality equipment built to last. Dixon offers a variety of products suitable for steel mills.
GSM Armored Hose

Sizes:
- 1/4" through 12" I.D.
Features:
- Extremely flexible armor protects from heat, slag splash, and harsh environments in mill applications
- Heat resistant to 1000°F (537°C)
- Temperature rating depends on specific applications, consult Dixon
Materials:
- Armor: Galvanized steel or stainless steel
- Wide selection of inner hoses specific to steel mill applications: industrial, hydraulic, metal, and PTFE
Dixon’s GSM armored hose was originally designed specifically for use in a steel mill. Read our blog post, A History and Overview of GSM Armored Hose, to learn more.
HTE-Series Correct Connect® Under Pressure Flush Face Female Plug

Sizes:
- Body: 3/8", 1/2", 5/8", 3/4", and 1"
Features:
- Can be connected with residual pressure in the plug up to 5,000 PSI
- Used in conjunction with Dixon HT-series and other ISO16028 couplers
- Smooth connection action up to full working pressure
- Flush face design is less susceptible to system contamination
- Compact design
- Threads: NPTF, BSPP, and ORB
HT-Series Correct Connect® Flush Face Flange Sleeve Coupler

Sizes:
- Body: 3/8", 1/2", 5/8", 3/4", and 1"
Features:
- Includes Correct Connect® color banding system
- Works with HT-series and HTE-series plugs
- ISO16028 flush face coupler x 3/8"-1" F-NPTF
- Flange makes it easy to grip with gloves to connect and disconnect, as well as twist the sleeve to lock and unlock the coupling connection
Material:
- Steel
Swivels

Sizes:
- 1" to 18"
Features:
- Full 360° rotational movement
- Precision-machined design ensures alignment and trouble-free service
- Various pressure seal designs to meet specific application requirements
- Hydrostatic testing is performed on all swivels before shipping
- Large bore swivels are also available, contact Dixon
Materials:
- Carbon steel, 316 stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and malleable iron
Heavy Duty EZ Boss-Lock Type D Couplers

Sizes:
- 3", 4", 6", and 8"
Features:
- Resistant to accidental disconnection when dragged
- 4 EZ Boss-Lock cam & groove handles enable increased working pressure
Material:
- 316 stainless steel
Venting EZ Boss-Lock

Sizes:
- 2", 3", and 4"
Features:
- EZLink® tabs are utilized as a secondary locking mechanism to capture the adapter in case of accidental uncoupling under pressure
- Designed vent paths to help control the direction of venting media
- EZ Boss-Lock cam arms for an additional level of safety
- Works with all standard cam & groove adapters
- Type B, C, D, and H
Materials:
- 356T6 aluminum and 316 stainless steel
Cam & Groove Swivels

Sizes:
- 2", 3", and 4"
Features:
- Live swivel is capable of 360-degree rotation under pressure
- Nitrile rubber X-ring seals at the swivel for reduced friction and high stability in dynamic applications
- Couplers include EZ Boss-Lock cam arms
- Type A, C, D, and E
Materials:
- 356T6 aluminum and 316 stainless steel
- Gasket: nitrile rubber and FKM
- Seal: nitrile rubber X-rings and FKM
Rapp-it

Features:
- No mixing or measuring is required; easy to apply
- Quickly contains leaking substances, keeping a workplace safe
- Tenacious bond: 5 to 10 minutes; functional cure: approx. 30 minutes
- Suitable for use on acid lines, gas, most diluted chemicals, seawater, fuels, and oil
- Resistant to hydrocarbons, ketones, esters, alcohols, halocarbons, aqueous salt solutions, and dilute acids/bases
- Suitable for wet or dry pipe: apply under fresh and saltwater
- Temperatures:
- Continuous -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 121°C)
- Intermittent -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 149°C)
- Heat resistance: 300°F (150°C)
Materials:
- Bandage: woven fiberglass
- Resin: water-activated polyurethane resin
Summary
Although it can be simplified into six steps, the steel manufacturing process is complex and requires reliable equipment designed to withstand the harsh environment encountered in steel mills. Dixon manufactures and supplies products for every stage of steel production. From armored hose, fire jackets, and sleeving, to hydraulic quick disconnects, specialty fluid transfer products, swivels, and fire equipment, we are committed to providing real solutions for real challenges in the steel processing market. For more information, visit dixonvalve.com or call 877.963.4966.